The way people make purchases online has changed substantially as they require speedy and low-cost delivery services, especially for daily use products such as groceries, pharma, and food. There is a strong market for these products and hyperlocal startups have recognized this opportunity. Businesses in hyperlocal commerce use technology to cut-down the delivery time of products and services. The key players in the hyperlocal space include Swiggy, Zomato, Grofers, Urban Clap, Dunzo, DailyNinja, and MilkBasket.
Seamless Service Experience is Critical
The businesses partner with vendors and develop easy-to-use apps to simplify the order process. The platforms also have capabilities such as accepting various modes of payments (typically includes cash on delivery) and providing live tracking. MilkBasket allows for a one-touch order experience for its users such that even elderly people can place an order using the app. Some food businesses like Zomato have introduced hygiene ratings for restaurants. Other initiatives such as good customer support and faster complaint resolution also help in building trust with customers.
Deal Activity
The companies in the hyperlocal space have been raising money for geographic expansion, acquisition of businesses and improving customer experience on their apps.
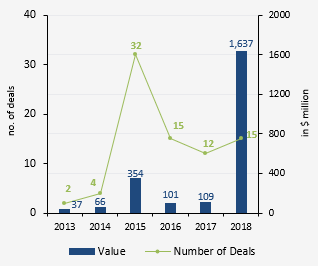
Businesses in hyperlocal commerce raised over $1.5 billion funding in 2018, making it one of the favored sectors for investors in 2018. The sector had 10 deals in the first half of 2018, raising USD 82.6 million, versus USD 15.2 million across 5 deals in the first half of 2017.
Venture Capitalists / Private Equity Deals
 Swiggy has raised USD 1.5 billion followed by Zomato raising USD 755.6 million, Grofers raising USD 461.8 million and Dunzo raising USD 30.7 million. Domestic and international funds are actively investing in the hyperlocal segment. The most active international funds in this segment are Tiger Global, Sequoia and Accel Partners.
Swiggy has raised USD 1.5 billion followed by Zomato raising USD 755.6 million, Grofers raising USD 461.8 million and Dunzo raising USD 30.7 million. Domestic and international funds are actively investing in the hyperlocal segment. The most active international funds in this segment are Tiger Global, Sequoia and Accel Partners.
The sector had 80 VC / PE deals in the period of 2013 to 2018 with a combined investment of USD 2.3 billion. Swiggy received the largest investment of USD 1 billion which included participation from Naspers, DST Global, and others in 2018.
The investments declined in 2016 and 2017 when investors were worried about the sustainability of businesses in this segment, however, the investments revived as larger players started investing in hyperlocal sector such as Google’s investment in Dunzo for USD 12.3 million at the end of 2017 and Grofers raising USD 61.6 million Series E funding led by Japan’s SoftBank Group in March’18.
Mergers and Acquisitions
The sector recorded 36 M&A deals in the period of 2013 to 2018, accumulating to USD 102 million. The businesses in the hyperlocal sector use funds raised by VCs for business acquisitions and expansion purposes. The M&A activity is expected to increase in the future as hyperlocal businesses need to acquire smaller businesses for expanding to new cities. Key M&A deals in 2018 were Ola (ANI Technologies Pvt. Ltd.) acquiring FoodPanda India (Pisces eServices Private Limited) for USD 32 million and Zomato (Zomato Media Private Limited) acquiring Tonguestun Food Network Private Limited for USD 18 million.
Opportunities
It is likely that the numbers of startups serving the food and grocery industry will increase in the coming years.
The Indian food and grocery market is a USD 300 billion segment in India and is expected to increase to USD 1 trillion by 2030. People have started to purchase groceries online with increasing mobile commerce and it’s the largest consumer segment by far.
Courier agents such as UBT international also use hyperlocal businesses to develop a PAN India presence and offer value-added services such as speedy pickups and packaging.
People in metro cities and tier 1 cities have embraced hyperlocal commerce due to better job opportunities, increasing internet usage, trending mobile commerce, and increasing per-capita disposable income. Hyperlocal commerce is beneficial for people who get settled in these cities as they can order food, grocery, medicines along with services such as plumbing and carpentry in just a few clicks. Hyperlocal businesses are also focusing on expansion in smaller cities in India, mostly through acquisitions.
Hyperlocal startups core business is making delivery models efficient to preserve margins and build volume. Employee costs are much lower in India. Businesses can achieve economies of scale by building order volume. Costs of hiring back office staff and delivery personnel are much lower in India as compared to other geographies, which gives an advantage to hyperlocal startups in India.
Key Challenges
One of the main challenged faced by hyperlocal startups is that 96% of commerce happens at mom-and-pop shops. This is mainly because of flexible credit terms and trust related factor. However, the transition is happening as people are moving towards making purchases online as the hyperlocal businesses offer deals on various products and price comparison functionality for its users.
Smaller cities in India have access to the internet, however, people are not adopting technology at a faster pace as compared to metro cities and tier 1 cities.
Currently, only 30 million out of 354 million online users in India, make purchases online, which is mainly due to lack of trust. Hyperlocal startups aim to increase the number to 130 million by addressing trust related issues.
There are many startups in the segment which could easily serve a location but couldn’t preserve margins with geographic expansion. Startups like Grofers decided to shut down its operations in 9 cities. Improving unit economics is also essential for geographic expansion for some businesses in this segment.
Outlook
The hyperlocal sector is focusing on improving its overall profitability by increasing sales volume, frequency of delivery, and making effective use of technology to enhance the customer experience. Hyperlocal segment is likely to experience a lot of consolidation in the coming years with an increasing number of players in this sector.
So far, the sector has done very well and appears to be very conducive for its growth but some problems need to be addressed by businesses to strive in this segment. Businesses in the hyperlocal segment are trying to use technology effectively to make the order process hassle-free. Seeing the participation of larger funds in the hyperlocal segment in India, gives a view of strong potential in this segment, however, the businesses still have to face some key challenges.
References
- EY E-commerce and Consumer Internet Sector – India Trendbook 2019
- Hyperlocal Commerce – innovationiseverywhere.com
- Crunchbase.com
- How Dunzo Got Google To Make its First Direct Investment in Dunzo, YourStory.com
- Why Hyperlocal delivery startups are grabbing investor eyeballs again, YourStory.com
- Why Kalaari Capital found value and invested in micro-delivery platform Milkbasket, YourStory.com
- Hyperlocal delivery turns new favourite for investors; Swiggy, Zomato, Grofers top funding chart, YourStory.com
Disclaimer:
This publication contains general information only and is based on the experiences and research of Anplify professionals. Anplify is not, by means of this publication, rendering business, financial, investment, or other professional advice or services. This publication is not a substitute for such professional advice or services, nor should it be used as a basis for any decision or action that may affect your business. Before making any decision or taking any action that may affect your business, you should consult a qualified professional advisor. Investments are subject to risk, including the loss of principal. Because investment return and principal value fluctuate, shares may be worth more or less than their original value. Some investments are not suitable for all investors, and there is no guarantee that any investing goal will be met. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. Talk to your financial advisor before making any investing decisions.





